Understanding Money Laundering
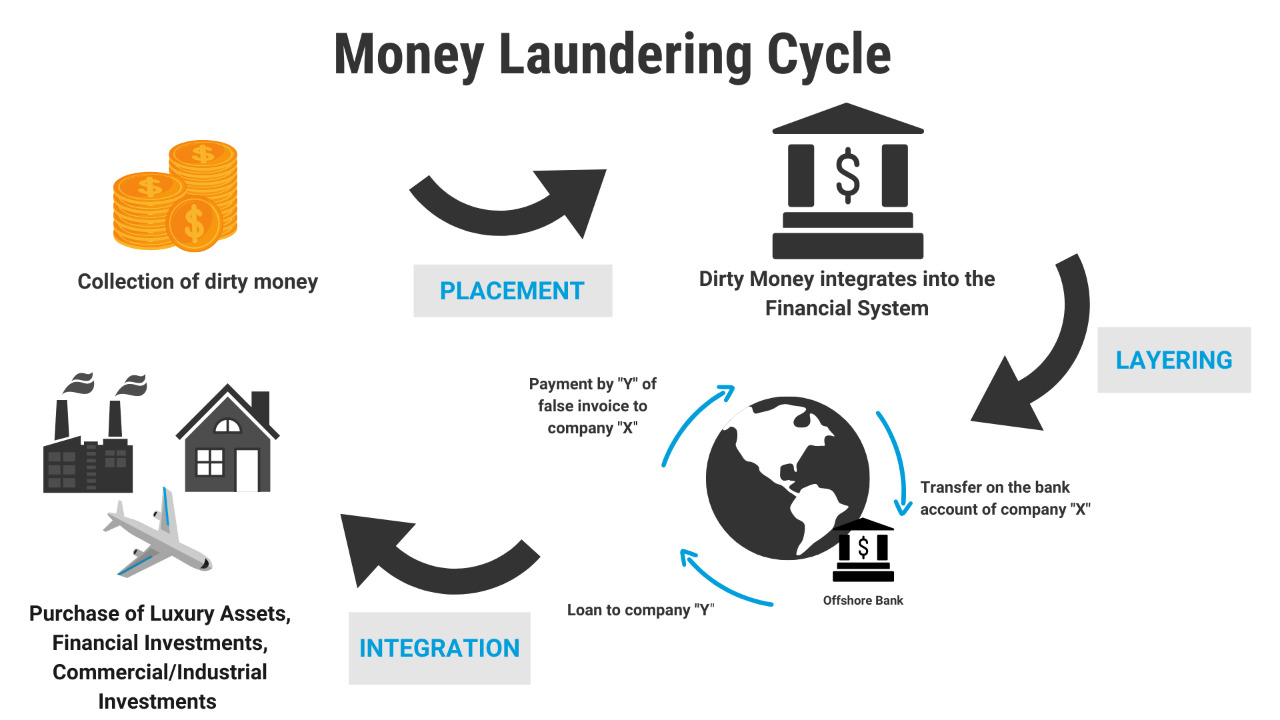
Money laundering involves three main stages: placement, layering, and integration. In the placement stage, illicit funds are introduced into the financial system, often through activities such as cash deposits, smurfing, or trade-based transactions. Pay stubs for Illinois here can be utilized as a method to create a false trail of legitimate income within the state. The layering stage aims to obscure the money’s source through complex transactions, multiple accounts, and international transfers. Finally, in the integration stage, the “cleaned” money is reintroduced into the legitimate economy, making it difficult to trace its illicit origins.
Red Flags and Indicators
Recognizing potential money laundering activities is crucial for prevention. Some common red flags include:
- Unusually large or frequent cash deposits or withdrawals.
- Transactions involving high-risk countries or individuals with questionable backgrounds.
- Rapid movement of funds through multiple accounts or complex transactions.
- Structuring transactions to evade reporting requirements.
- Unexplained transfers or wire transactions with no apparent business rationale.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance Measures

Governments and financial institutions play a crucial role in preventing money laundering through robust regulatory frameworks and compliance measures. Some key initiatives include:
- Know Your Customer (KYC): Implementing rigorous customer due diligence procedures to verify the identity and source of funds for individuals and businesses.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Policies: Establishing comprehensive AML policies that outline procedures, risk assessments, and internal controls to detect and report suspicious transactions.
- Reporting Obligations: Requiring financial institutions to report suspicious activities to the relevant authorities, such as Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs).
- Enhanced Due Diligence: Implementing additional scrutiny for high-risk customers, politically exposed persons (PEPs), and correspondent banking relationships.
- International Cooperation: Promoting collaboration among countries through information sharing, extradition agreements, and mutual legal assistance to combat cross-border money laundering.
Technology and Data Analytics
Advancements in technology and data analytics have significantly contributed to anti-money laundering efforts. Some tools and techniques include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Utilizing AI algorithms to analyze large volumes of data and identify patterns, anomalies, and potential money laundering activities.
- Blockchain Technology: Leveraging the transparency and immutability of blockchain to enhance the traceability and accountability of financial transactions.
- Big Data Analysis: Harnessing the power of big data to identify suspicious patterns, conduct network analysis, and improve risk assessments.
- Risk-Based Approach: Utilizing data-driven risk assessments to allocate resources effectively and focus on high-risk areas and individuals.
Conclusion
Money laundering poses a significant threat to global financial systems and economies. Preventing and combating money laundering requires a multifaceted approach involving robust regulatory frameworks, compliance measures, technological advancements, and international cooperation. By implementing preventive measures and remaining vigilant, we can work towards creating a more transparent and secure financial environment, deterring criminals from exploiting the system, and safeguarding the integrity of our economies.
